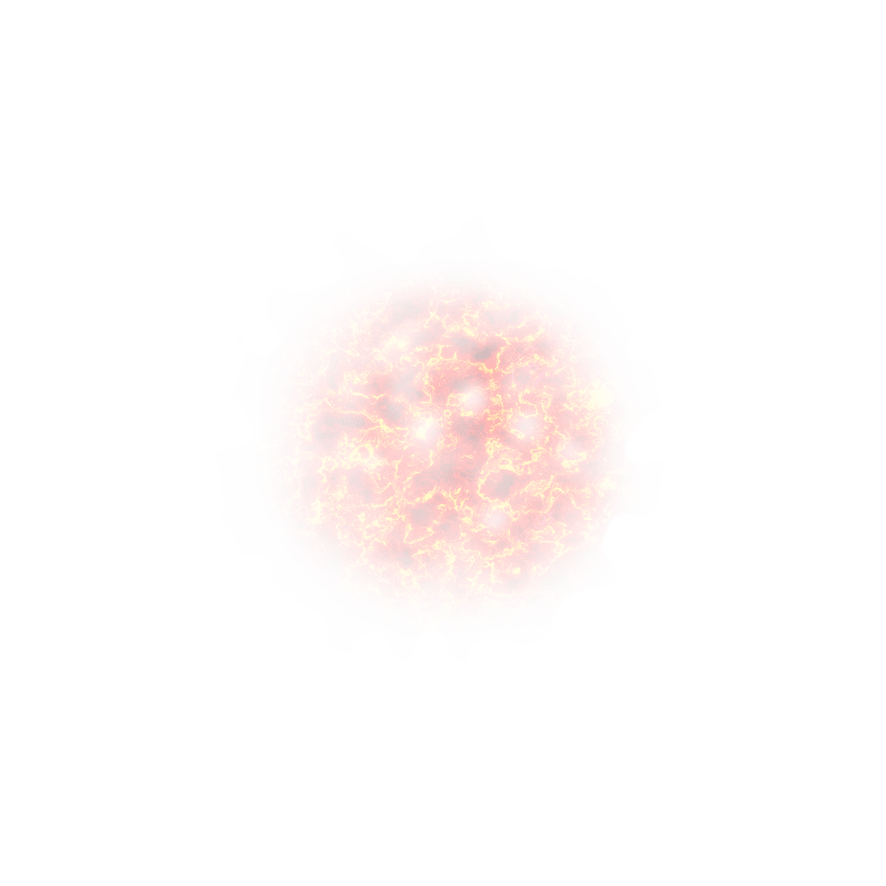
The phenomenon of underreporting in the context of biomedical research has been widely studied, at least since the works of Bernard et. al. in 2011 [2]. A slightly more recent reference is Fernández-Fontelo et. al. in 2016 [4], where a very simple mechanism is proposed to model the phenomenon. Let us consider a hidden process (the real daily number of positive cases, which is not observable since the entire population of interest is not tested daily) ![]() with an autoregressive structure of order 1, for integer data and with Poisson innovations, Po- INAR (1):
with an autoregressive structure of order 1, for integer data and with Poisson innovations, Po- INAR (1):
![]()
where ![]() is a fixed parameter,
is a fixed parameter, ![]() Poisson(
Poisson(![]() ), i.i.d., independent of
), i.i.d., independent of ![]() and
and ![]() is the operator of thinning binomial:
is the operator of thinning binomial:
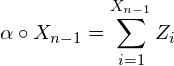
con ![]() variables aleatorias i.i.d. con distribución de Bernoulli
variables aleatorias i.i.d. con distribución de Bernoulli![]() .
.
El proceso INAR(1) es una cadena de Markov homogénea con probabilidades de transición
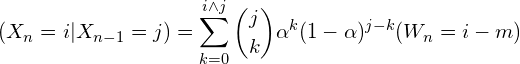
La esperanza y varianza del operador de thinning binomial son
![]()
y
![]()
Un esquema simple de infra-reporte
The underreporting phenomenon is modeled assuming that the observed counts have the following form:
(1) 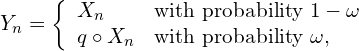
where ![]() y
y ![]() represent the frequency and intensity of the underreported process. That is, for each
represent the frequency and intensity of the underreported process. That is, for each ![]() , a
, a ![]() can be observed with a probability
can be observed with a probability ![]() , and a
, and a ![]() -thinning of
-thinning of ![]() with probability
with probability ![]() , regardless of previous
, regardless of previous ![]() . Therefore, what is observed (the reported counts) is
. Therefore, what is observed (the reported counts) is
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[Y_n = (1- \uno_n)X_n + \uno_n \sum_{j=1}^{X_n} \xi_j \quad\quad \uno_n\sim\mbox{Bern}(\omega), \quad \xi_j\sim\mbox{Bern}(q)\]](https://underreported.cs.upc.edu/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-250849eba859986f19506d471faf11ce_l3.png)
Model properties
The expectation and variance of the INAR (1) ![]() process with Poisson innovations (
process with Poisson innovations (![]() ) is
) is ![]() . The autocovariances and autocorrelations are
. The autocovariances and autocorrelations are
![]()
![]()
Thus, the autocorrelation function ![]() is a multiple of
is a multiple of ![]() :
:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\rho_Y(k)=\frac{(1-\alpha)(1-\omega(1-q))^2}{(1-\alpha)(1-\omega(1-q))+\lambda(\omega(1-\omega)(1-q)^2)}\alpha^{|k|}=c(\alpha,\lambda,\omega,q)\alpha^{|k|}.\]](https://underreported.cs.upc.edu/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e29d0096f34f8961001d4746695ae72d_l3.png)
The shape of the expected value ![]() also allows to obtain predictions for
also allows to obtain predictions for ![]() having seen until
having seen until ![]() .
.
Parameter estimation
The marginal distribution of ![]() is a mixture of two Poission distributions.
is a mixture of two Poission distributions.
(2) 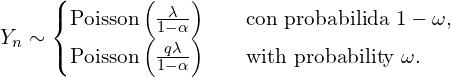
When ![]() the distribution of
the distribution of ![]() Poisson zero-inflated. From the mixture we can have preliminary estimates for the parameters that will later be used in a calculation of the maximum likelihood estimators. The plausibity of
Poisson zero-inflated. From the mixture we can have preliminary estimates for the parameters that will later be used in a calculation of the maximum likelihood estimators. The plausibity of ![]() is very complicated,
is very complicated,
![]()
and to calculated the forward algorithm ~\cite{lystig02} is widely used in the context of hidden Markov models. The probabilities of forward are
(3) 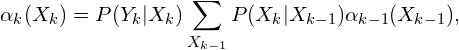
con ![]() . Therefore the plausibity is
. Therefore the plausibity is
![]()
![]() y
y ![]() these are the so-called emission and transition probabilities. Transition probabilities are calculated as follows:
these are the so-called emission and transition probabilities. Transition probabilities are calculated as follows:
(4) 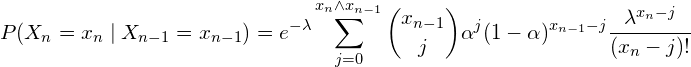
and the emision ones
(5) 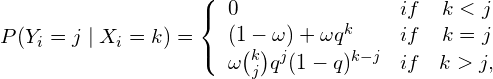
Rebuilding the hidden chain 
To reconstruct the hidden series ![]() , the \textbf{Viterbi} [10] algorithm is used as described previously.
, the \textbf{Viterbi} [10] algorithm is used as described previously.
The main idea to reconstruct the latent chain ![]() which maximizes the probability of the latent process given the observations
which maximizes the probability of the latent process given the observations ![]() , assuming that the parameters are known.
, assuming that the parameters are known.
Bibliografía
[2] Bernard H,Werber D, Hoehle M. Estimating the under-reporting of norovirus illness in Germany utilizing enhanced awareness of diarrhoea during a large outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli O104: H4 in 2011-a time series analysis. BMC
Infectious Diseases 2014; 14:116. DOI:10.1186/1471-2334-14-116.
[3] Fan, C. et al. Prediction of Epidemic Spread of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Driven by Spring Festival Transportation in China: A Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, (2020).
[4] Fernández-Fontelo A., Cabaña A., Puig P., Moriña D. Under-reported data analysis with INAR-hidden Markov chains
Statistics in Medicine (2016), vol. 35, Issue 26, 4875-4890.
[5] Fernández‐Fontelo, A., Cabaña, A., Joe, H., Puig, P. & Moriña, D. Untangling serially dependent underreported count data for gender‐based violence. Stat. Med. 38, 4404–4422 (2019).
[6] Moriña, D., Fernández-Fontelo, A., Cabaña, A. & Puig, P. New statistical model for misreported data with application to current public health challenges. Submitted to Statistical Methods in Medical Research, (2020).
[7] Moriña, D., Fernández-Fontelo, A., Cabaña, A., Puig, P., Monfil, L., Brotons, M. & Diaz, M. Quantifying the underreporting of genital warts cases. Submitted to the European Journal of Epidemiology (2020).
[8] Kermack W. O., McKendrick A. G. (1927). A Contribution to the Mathematical Theory of Epidemics. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 115 (772): 700–721.
[9] T.C. Lystig, J.P. Hughes (2002), Exact computation of the observed information matrix for hidden Markov models, J. of Comp.and Graph. Stat.
[10] Viterbi, A.J. (1967), Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13, 260D269.